Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagame, Yuichiro
Nature Chemistry, 8(3), P. 282, 2016/03
We summarize the studies of element 103, lawrencium: discovery or synthesis in nuclear reactions, historical argument for recognition as a new element, nuclear and chemical studies of lawrencium isotopes, and recently measured ionization energy. Based on the studies so far performed, we introduce a debate that has emerged over the place in the periodic table.
 Mn
Mn N
NHwang, J. I.*; Ishida, Yukiaki*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Hirata, Gen*; Takubo, Ko*; Mizokawa, Takashi*; Fujimori, Atsushi; Okamoto, Jun; Mamiya, Kazutoshi*; Saito, Yuji; et al.
Physical Review B, 72(8), p.085216_1 - 085216_6, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:87.86(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 A
A MnO
MnO (A=Ca,Sr)
(A=Ca,Sr)Kang, J.-S.*; Kim, J. H.*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Kasai, Shuichi*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Han, S. W.*; Kim, K. H.*; Choi, E. J.*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*; Muro, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 68(1), p.012410_1 - 012410_4, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:68.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Yasuji; Kaneyoshi, Takahiro*; Gullikson, E. M.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Spectrochimica Acta, Part A, 59(9), p.1951 - 1957, 2003/07
Angle-resolved soft X-ray emission and absorption spectra in the BK and NK regions of hexagonal BN were measured using polarized synchrotron radiation. The take-off/incident-angle-dependence on the spectral features in both X-ray emission and absorption is clearly observed. The configuration of the s and p orbitals, which were calculated using discrete variaional (DV) -Xa molecular orbital calculations, explains the angle-resolved soft X-ray emission and absorption spectra. The relative peak intensity of the 394-eV peak in the NK X-ray emission provides useful information about the BN layer ordering.
 and Ac
and Ac hydrate models
hydrate modelsMochizuki, Yuji*; Tsushima, Satoru*
Chemical Physics Letters, 372(1-2), p.114 - 120, 2003/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:39.19(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Tanaka, Tomoaki*; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Shimada, Hiromichi*; Saito, Takeru
Analytical Sciences (CD-ROM), 17(Suppl.), p.119 - 121, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Yasuji; Hirono, Shigeru*; Umemura, Shigeru*; Ueno, Yuko*; Hayashi, Takayoshi*; Grush, M. M.*; Gullikson, E. M.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Carbon, 39(9), p.1403 - 1407, 2001/06
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:58.33(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Yasuji; Ueno, Yuko*; Ishiwata, Yoichi*; Eguchi, Ritsuko*; Watanabe, Masamitsu*; Shin, S.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Carbon, 39(9), p.1359 - 1402, 2001/06
no abstracts in English
Muramatsu, Yasuji
Advances in X-Ray Chemical Analysis, Japan, 32, p.147 - 159, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
Tejima, Shogo
JNC TN8400 2000-029, 54 Pages, 2000/10
This report describes the study done by the author as a postdoctoral research associate at Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute. This report is divided into three parts: construction of a relativistic band calculation formalism based on the density functional theory, using this method, investigation of the electrical properties for ferromagnetic UGe and antiferromagnetic UO
and antiferromagnetic UO . (1)A relativistic band calculation (RBC) method. Band calculations for the s, p, and d electric structure have been developed well in the practical application and theoretical study. But band calculation method treating magnetic 5f electrons as actinide compounds are complicated and needed relativistic approach, so it is behind with the study of the 5f system. In this study we construct the relativistic band calculationformalism valid for magnetic 5f electrons. (2)Electric properties of UGe
. (1)A relativistic band calculation (RBC) method. Band calculations for the s, p, and d electric structure have been developed well in the practical application and theoretical study. But band calculation method treating magnetic 5f electrons as actinide compounds are complicated and needed relativistic approach, so it is behind with the study of the 5f system. In this study we construct the relativistic band calculationformalism valid for magnetic 5f electrons. (2)Electric properties of UGe . The actinide compounds UGe
. The actinide compounds UGe is ferromagnetic, so the theoretical analysis is not well yet. The electric structure and fermi surface of UGe
is ferromagnetic, so the theoretical analysis is not well yet. The electric structure and fermi surface of UGe are analyzed using the RBC. The theoretical results show that UGe
are analyzed using the RBC. The theoretical results show that UGe is heavy electron with the 5f character and are agreement with experimental one. (3)Electric structure of nuclear fuel UO
is heavy electron with the 5f character and are agreement with experimental one. (3)Electric structure of nuclear fuel UO . It is important to understand the mechanism of the thermal conductivity of nuclear fuel as antiferromagnetic UO
. It is important to understand the mechanism of the thermal conductivity of nuclear fuel as antiferromagnetic UO . The UO
. The UO band calculation reflecting the thermal properties, into account of relativistic effect, have not done yes. So using the RBC the detailed electric structure of UO
band calculation reflecting the thermal properties, into account of relativistic effect, have not done yes. So using the RBC the detailed electric structure of UO are obtained.
are obtained.
Muramatsu, Yasuji; Takenaka, Hisataka*; Ueno, Yuko*; Gullikson, E. M.*; Perera, R. C. C.*
Applied Physics Letters, 77(17), p.2653 - 2655, 2000/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:51.49(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
*; Noro, Hisato*; Nagoshi, Masayasu*; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Baba, Yuji; Sasaki, Teikichi
Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 88-91, p.467 - 471, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.21(Spectroscopy)no abstracts in English
Saito, Junichi; Kano, Shigeki
PNC TN9410 97-073, 69 Pages, 1997/07
In order to understand the effect of implanted atom in ceramics and metals on the sodium corrosion, the electronic structures of un-implanted and implanted materials were calculated using DV-X cluster method which was one of molecular orbital calculations. The calculated materials were
cluster method which was one of molecular orbital calculations. The calculated materials were  -Si
-Si N
N ,
,  -SiC and
-SiC and  -SiC as ceramics, and f.c.c.Fe, b.c.c.Fe and b.c.c. Nb as metals. An Fe, Mo and Hf atom for ceramics, and N atom for metals were selected as implanted atoms. It is known that these metallic elements have exhibited the excellent corrosion resistance against liquid sodium in previous experiments. The summary of results is shown as follows. Energy levels of implanted atom appeared in or near energy band gap in ceramics. The change of ionicities of each element which showed amount of transferred charges and bond order which showed the covalent bond strength between atoms depended on substrates and implanted atoms. The strength of ionic bonding between atoms reduced in
-SiC as ceramics, and f.c.c.Fe, b.c.c.Fe and b.c.c. Nb as metals. An Fe, Mo and Hf atom for ceramics, and N atom for metals were selected as implanted atoms. It is known that these metallic elements have exhibited the excellent corrosion resistance against liquid sodium in previous experiments. The summary of results is shown as follows. Energy levels of implanted atom appeared in or near energy band gap in ceramics. The change of ionicities of each element which showed amount of transferred charges and bond order which showed the covalent bond strength between atoms depended on substrates and implanted atoms. The strength of ionic bonding between atoms reduced in  -Si
-Si N
N , as ionicities of constituent atom decreased by the implanted atom. The decreases of ionicity depended on implanted atoms and Hf implantation showed the largest decrease in implanted atoms. The bond order in
, as ionicities of constituent atom decreased by the implanted atom. The decreases of ionicity depended on implanted atoms and Hf implantation showed the largest decrease in implanted atoms. The bond order in  -Si
-Si N
N and
and  -SiC decreased by the implantation. When the implanted atom occupied at substitutional site in
-SiC decreased by the implantation. When the implanted atom occupied at substitutional site in  -SiC, the ionicities decreased but the bond order increased. Electron state densities of s and p components of implanted N atom appeared lower energy level than that of d component of constituent Fe (or Nb) atoms. The charge transfer took place to N atom from surrounding Fe (or Nb) atoms. Thus the ionicity of N atom was larger than mother metal. The bond order between mother elements reduced by N implantation. In particularly, there were significant decreases of bond order in b.c.c. Fe and b.c.c. Nb. Hence, the bond order in whole cluster decreased largely except for f.c.c. Fe. Consequently, it is ...
-SiC, the ionicities decreased but the bond order increased. Electron state densities of s and p components of implanted N atom appeared lower energy level than that of d component of constituent Fe (or Nb) atoms. The charge transfer took place to N atom from surrounding Fe (or Nb) atoms. Thus the ionicity of N atom was larger than mother metal. The bond order between mother elements reduced by N implantation. In particularly, there were significant decreases of bond order in b.c.c. Fe and b.c.c. Nb. Hence, the bond order in whole cluster decreased largely except for f.c.c. Fe. Consequently, it is ...
*; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAERI-Data/Code 96-017, 62 Pages, 1996/03
no abstracts in English
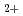 and O
and O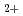 ion-implanted Si(100)
ion-implanted Si(100)Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Baba, Yuji; Sasaki, Teikichi
Surface and Interface Analysis, 23, p.381 - 385, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:53.88(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
G.T.Seaborg*; Yamashita, Toshiyuki
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 31(7), p.805 - 811, 1989/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato
no journal, ,
Soft X-ray emission spectroscopy is a powerful tool for a nondestructive evaluation technique for the electronic structure of a buried layer such as an absorber in thin-film solar cells. In our previous study, a wide band W/B C multilayer grating spectrograph has been successfully developed, but the detection area cannot cover the energy range of 1-3.5 keV, in which the characteristic X-ray lines of Cu-
C multilayer grating spectrograph has been successfully developed, but the detection area cannot cover the energy range of 1-3.5 keV, in which the characteristic X-ray lines of Cu- (0.9 keV), In-
(0.9 keV), In- (3.4 keV), Se-
(3.4 keV), Se- (1.4 keV) from a CIS solar cell are included. We newly developed a wide band Ni/C multilayer grating to cover the energy range from 1 keV to 3.5 keV at a constant incidence angle.
(1.4 keV) from a CIS solar cell are included. We newly developed a wide band Ni/C multilayer grating to cover the energy range from 1 keV to 3.5 keV at a constant incidence angle.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Koeda, Masaru*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Sasai, Hiroyuki*; Oue, Yuki*; Yonezawa, Zeno*; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; Terauchi, Masami*; Takahashi, Hideyuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
We developed a flat-field spectrograph for soft X-ray emission spectroscopy in 50-4000 eV to be able to be installed in electron microscopes. The diffraction efficiency and resolving power of the spectrograph were evaluated by using synchrotron radiation and laser produced plasma soft X-ray light sources, respectively. The spectral performance of the spectrograph installed in a transmission electron microscope was evaluated. The K emission spectrum from metallic lithium and the L emission lines of indium and tin from tin-doped indium oxide (ITO) were clearly observed around 54 eV and 3.6 keV, respectively.
Imazono, Takashi; Koike, Masato; Kuramoto, Satoshi*; Nagano, Tetsuya*; Koeda, Masaru*
no journal, ,
We designed a flat-field soft X-ray spectrometer to detect  X-rays from 1 to 3.5 keV emitted from the CIS absorber consisting of Cu, In, and Se in a CIS solar cell. We invented a wideband multilayered grating, which was coated with an aperiodic Ni/C multilayer on a laminar-type varied-line-spacing grating, to cover the whole energy range at a constant angle of incidence. Since there is no mechanical movement of the grating and a detector, the spectrometer can provide quick and accurate measurements in the 1-3.5 keV range as well as high resolution analysis.
X-rays from 1 to 3.5 keV emitted from the CIS absorber consisting of Cu, In, and Se in a CIS solar cell. We invented a wideband multilayered grating, which was coated with an aperiodic Ni/C multilayer on a laminar-type varied-line-spacing grating, to cover the whole energy range at a constant angle of incidence. Since there is no mechanical movement of the grating and a detector, the spectrometer can provide quick and accurate measurements in the 1-3.5 keV range as well as high resolution analysis.
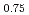 K
K Fe
Fe As
As due to electron correlation effects
due to electron correlation effectsMurai, Naoki; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Suzuki, Katsuhiro*; Nakajima, Masamichi*; Ikeda, Hiroaki*; Ideta, Shinichiro*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*
no journal, ,
We report inelastic neutron scattering (INS) study of hole-doped iron-based superconductor Ba K
K Fe
Fe As
As (x = 0.25). The INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A random phase approximation (RPA) treatment of the dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the band renormalization factor of 3 derived from angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) measurements on the same sample, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that the Fe-3d bandwidth narrowing due to electron correlation is directly reflected in the spin excitation energy scale. We will discuss the current state of our analysis relating the magnetic response to the underlying electronic structure of the materials.
(x = 0.25). The INS data show a spin-wave-like dispersive feature, with a zone boundary energy of 200 meV. A random phase approximation (RPA) treatment of the dynamical spin susceptibility, incorporating the band renormalization factor of 3 derived from angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) measurements on the same sample, provides a reasonable description of the observed spin excitations. This analysis shows that the Fe-3d bandwidth narrowing due to electron correlation is directly reflected in the spin excitation energy scale. We will discuss the current state of our analysis relating the magnetic response to the underlying electronic structure of the materials.